Medical coding
Introduction
Viedoc Coder allows you to code data, such as Adverse Events, Medical History, and Concomitant Medications, in a standardized way. You can access Viedoc Coder from the landing page.
The Viedoc Coder page displays metrics about coding, for example, the number and percentage of items that have been coded and approved. There is one set of metrics for each coding scope. The metrics displayed are based on the data and sites that you have permission to view.
Note!
- You can only access Viedoc Coder if permission to view, perform, and/or approve medical coding is activated for your role. If you do not see the medical coding icon, you do not have a role with medical coding permissions.
- The MedDRA Chinese translation version 26.0 and onwards has the term 牙开𬌗. This term will be displayed as 牙开 in the Viedoc system, as the last character is not supported.
Viedoc Coder
Overview
| 1. |
To open Viedoc Coder, select the dictionary icon: 
Viedoc Coder opens in a new window: 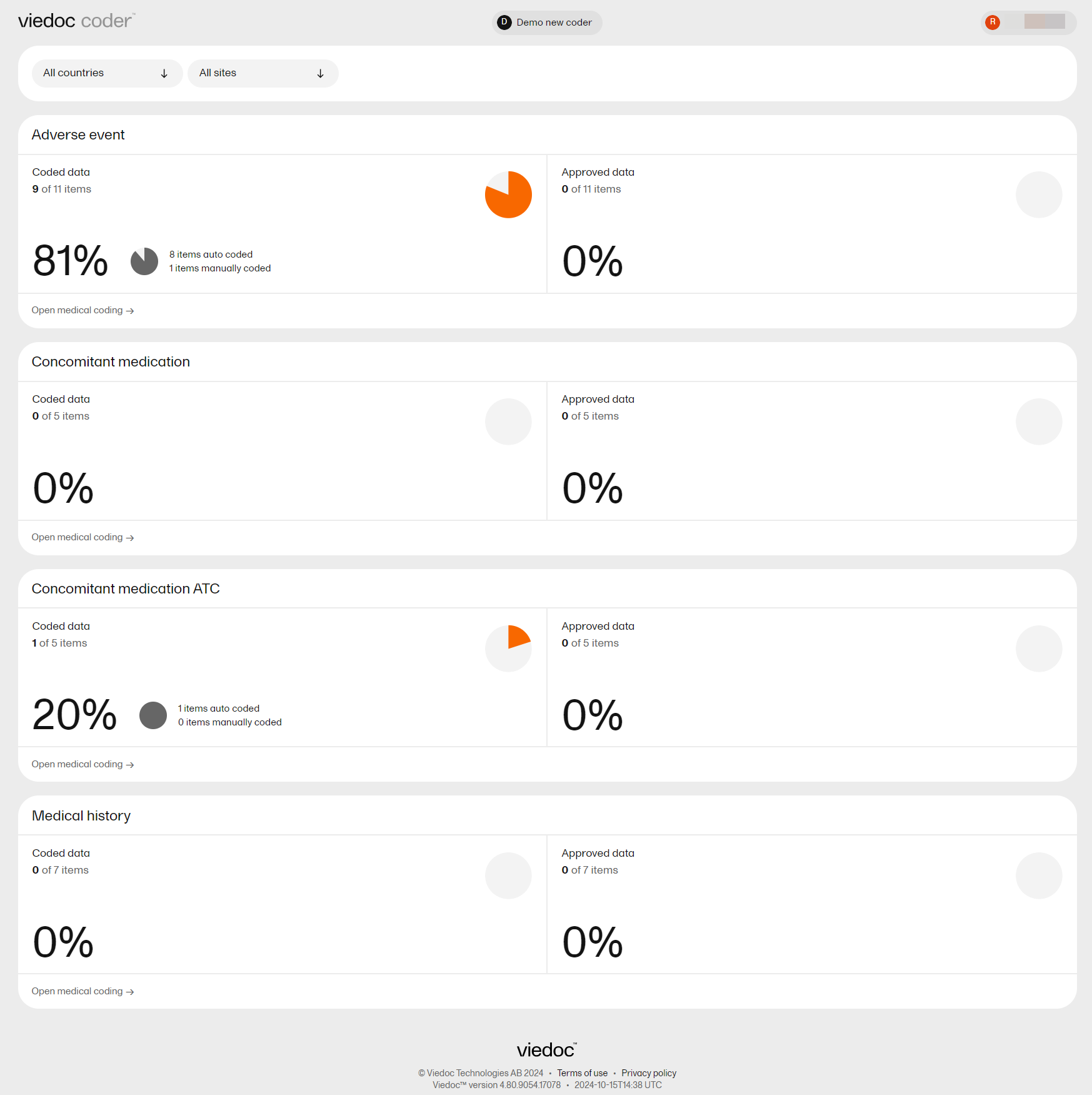
|
| 2. |
Select Open medical coding on a scope: 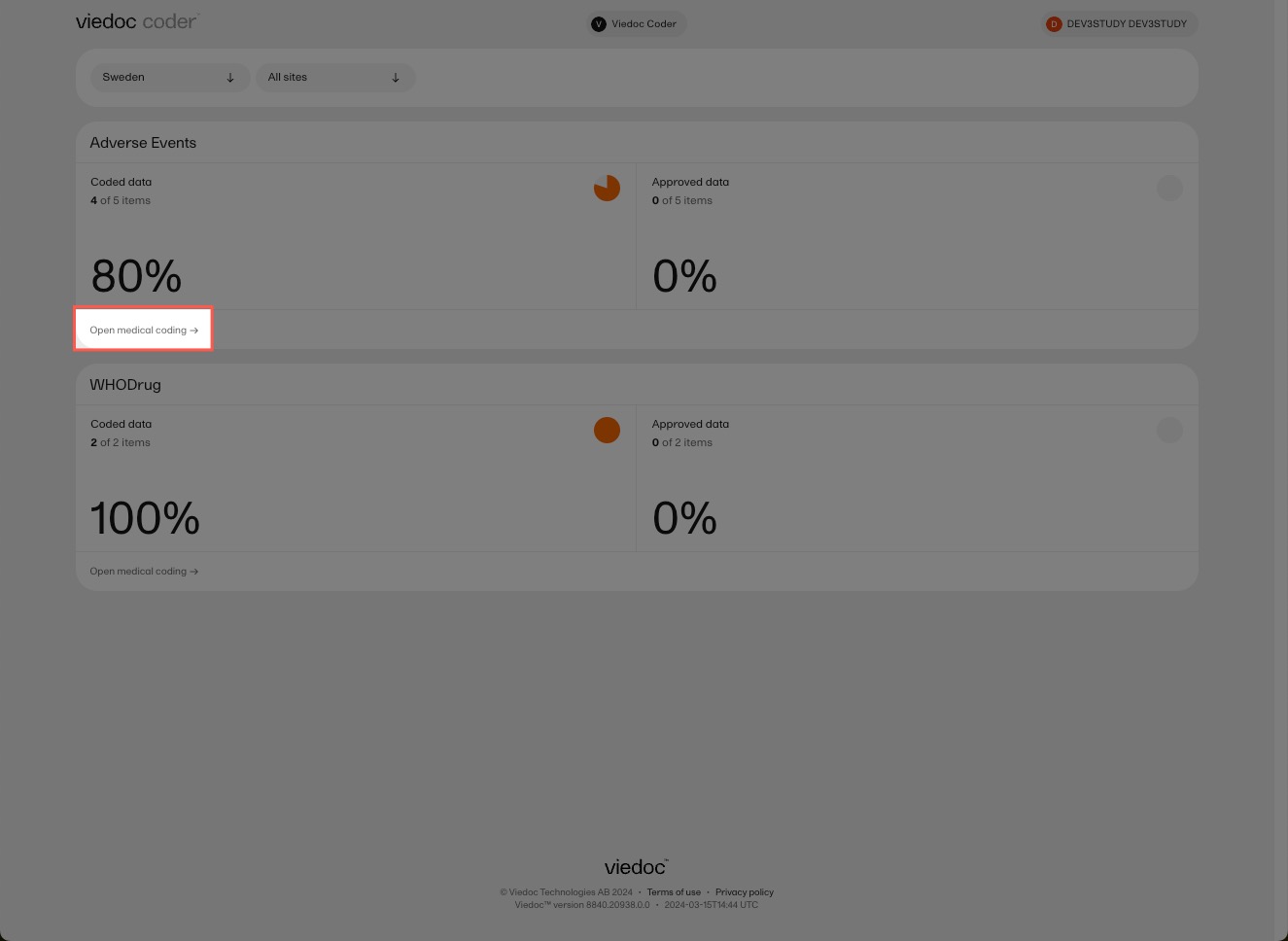
Viedoc Coder displays a table that lists all of the items to be coded in the Value column. 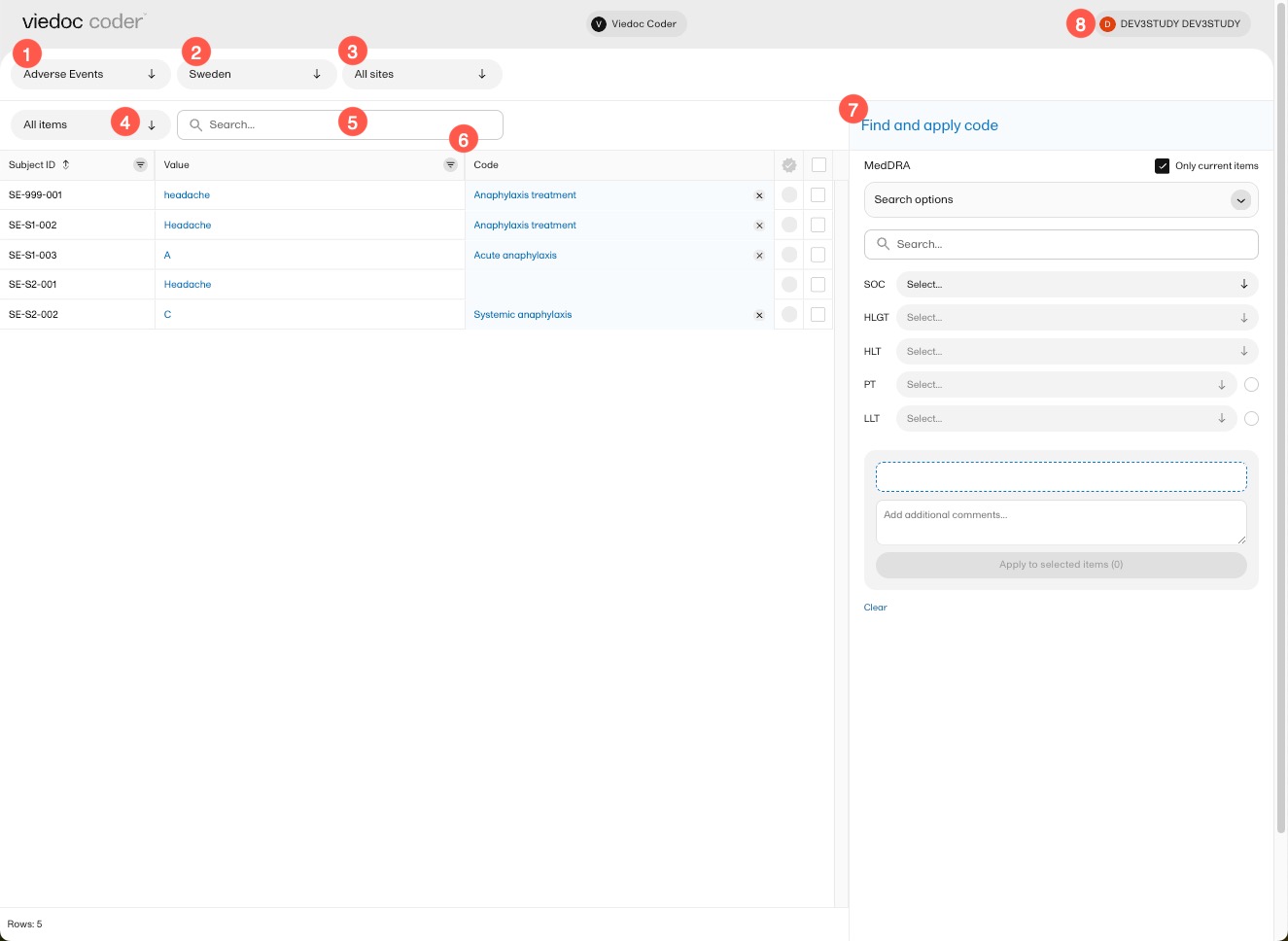
|
In Viedoc Coder, you can:
1. Select the coding scope (the data) to be coded.
2. Select to display items from all countries or from an individual country.
3. Select to display items from all sites or from an individual site.
4. Select to display all uncoded (and rejected) items, all coded items, all approved items, or all items.
5. Perform a text search among all values of the items.
6. If configured for your study, there can be additional columns included with supporting values for the coding, for example route, indication, or other.
7. Find and apply codes (see Finding and applying a medical code).
8. Select here to change the settings of Viedoc, access the help center, or logout of Viedoc.
When applying codes, you can:
- Add a comment - an interpretation or explanation of the value that you have assumed in order to code.
- Add multiple codes to one value.
See Finding and applying a medical code.
What do the symbols and colors mean?
In Viedoc Coder, you can find the following symbols:
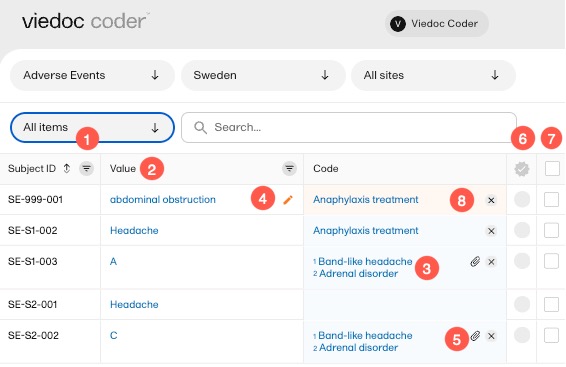
1. The three horizontal lines is a filter function. Select the symbol to open a dropdown list with a search field and a list of selectable items.
2. Fields have a sorting function which will list its contents in ascending and descending order. This function is not available for all columns.
3. A numbered list in the code field means that there is more than one medical code applied to that value.
4. An orange pen icon in the value field, together with a light orange background in the code field, means that the value (form item) has been changed in Viedoc Clinic by the Investigator after the item was coded. The applied code may not be correct anymore and the item should be re-coded.
5. A clip icon in the code field means that an interpretation has been added. Move the mouse pointer over the clip icon to view the contents of the interpretation.
6. An activated tick mark indicates that the coding has been approved.
7. The checkbox is used to mark the values to which a selected code should be applied.
8. The white cross in a grey circle is used to delete the applied code.
Finding and applying a medical code
This section gives an example of medical coding of adverse events using the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) and an example of medical coding of concomitant medication using the World Health Organization Drug Dictionary (WHODrug). The coding procedure is similar even if you are using other types of dictionaries.
Note! You can see the terminology version for both MedDRA and WHODrug if you hover over the i-icon in the dictionary panel:
A use case for coding with the MedDRA dictionary
Searching for a code
To find a code that you want to apply to a value, use the Find and apply code section.
There are three search options available:
- Contains - the search will return all entries that contain the text typed in the search field. This is the default option.
- Begins with - the search will return all entries that begin with the text typed in the search field.
- Exact match - the search will return all entries that exactly match the text typed in the search field.
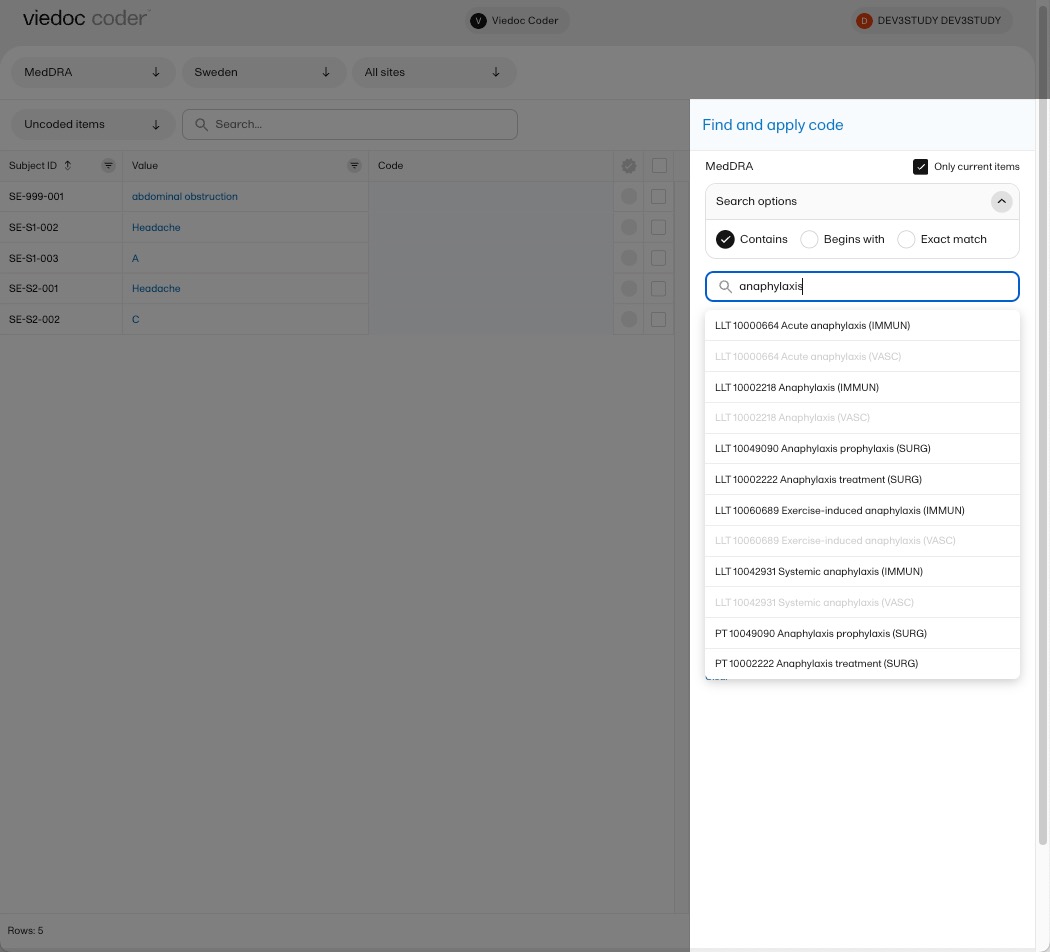
You can search for codes or (substrings of) terms in the Search field. Codes matching the term will be listed in a dropdrown list that deploys from the Search field. If a term is linked to multiple System Organ Classes (SOCs), the code that links to the primary SOC is displayed in black, while the codes that link to secondary SOCs are displayed in grey.
Searching is not case sensitive. If you type in "Anaphylaxis", the search can return results such as "anaphylaxis" and "Anaphylaxis".
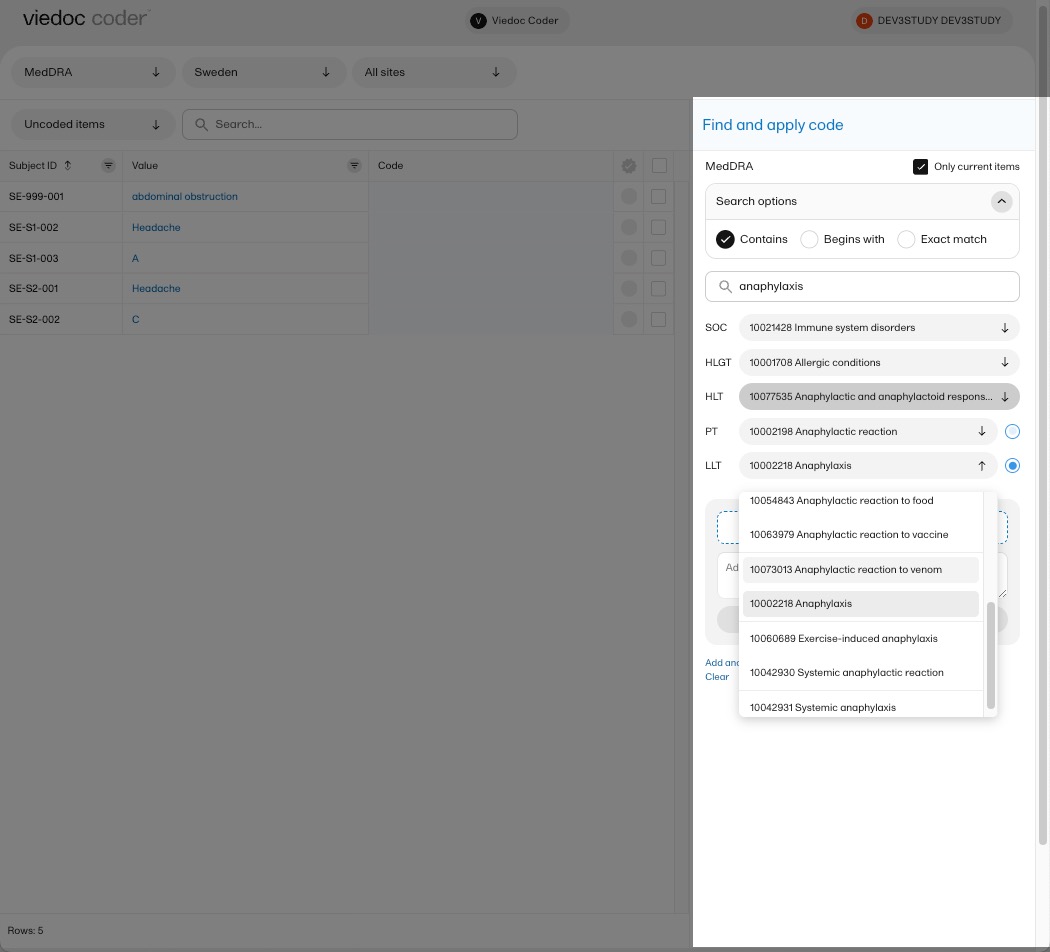
You can also search a code by selecting the System Organ Class (SOC), High Level Group Term (HLGT), High Level Term (HLT), Preferred Term (PT) and Low Level Term (LLT) using the dropdown lists below the search field.
By default, the search returns low level terms (LLTs) that have the status 'current' in the MedDRA dictionary. You can search among non-current MedDRA codes (that is, terms that are vague, ambiguous, truncated, abbreviated, out-dated, or misspelled and thus no longer used), by clearing the checkbox for Only current items.
Selecting a code
Select the code you would like to apply. The details of this code appear in the fields below the search field.
You can select to use the Preferred Term (PT) or the Low Level Term (LLT) by selecting one of the blue radio buttons next to the PT and LLT fields, as shown below:
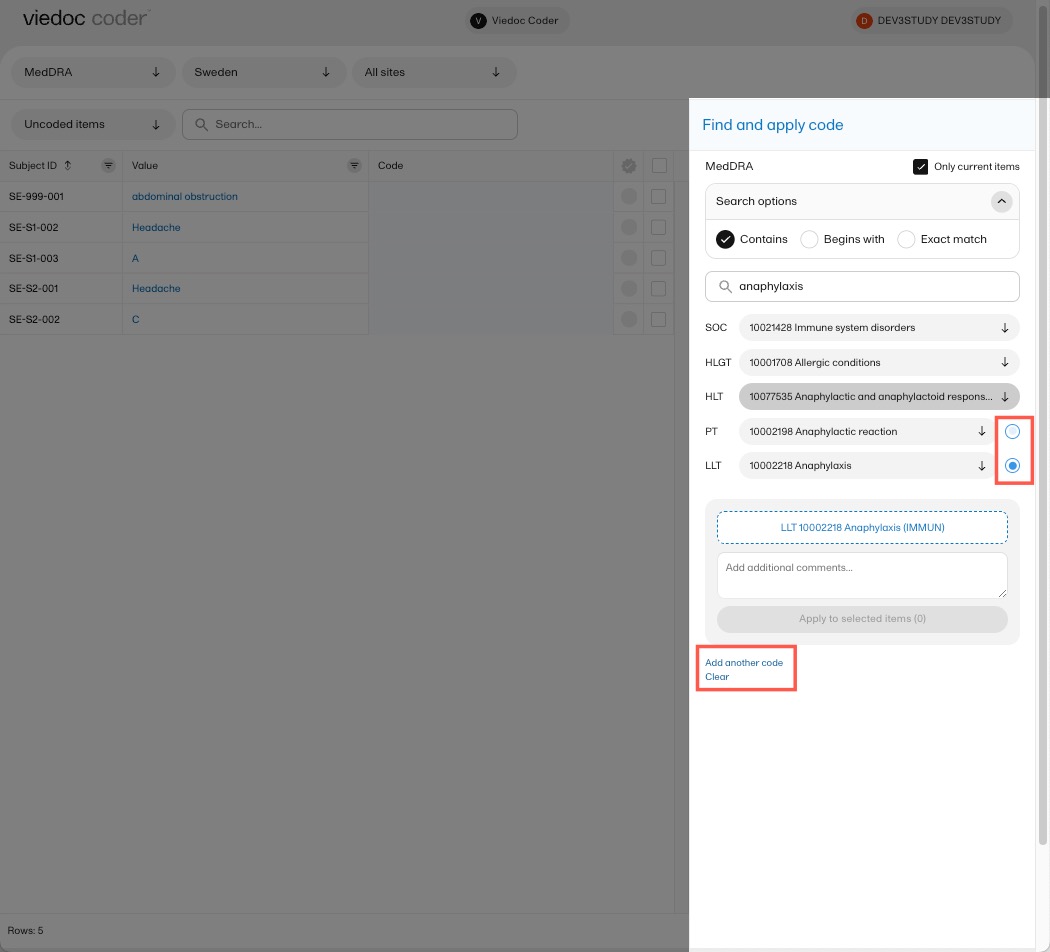
If you would like to add more than one code to the same value, select Add another code.
If you would like to add an interpretation, that is, a comment or explanation of the selected code, select Add interpretation and type your interpretation in the field.
You can reset your selections by selecting Clear.
Tip! If you want to apply a code that has been used before, select that code in the left side of the table. The Find and apply code section is then automatically populated with the selections for that code.
Applying a code
To apply a selected code, select the checkboxes for the value or values you want to apply that code to, and select Apply to selected items. The selected code will be applied to the selected subjects and values.
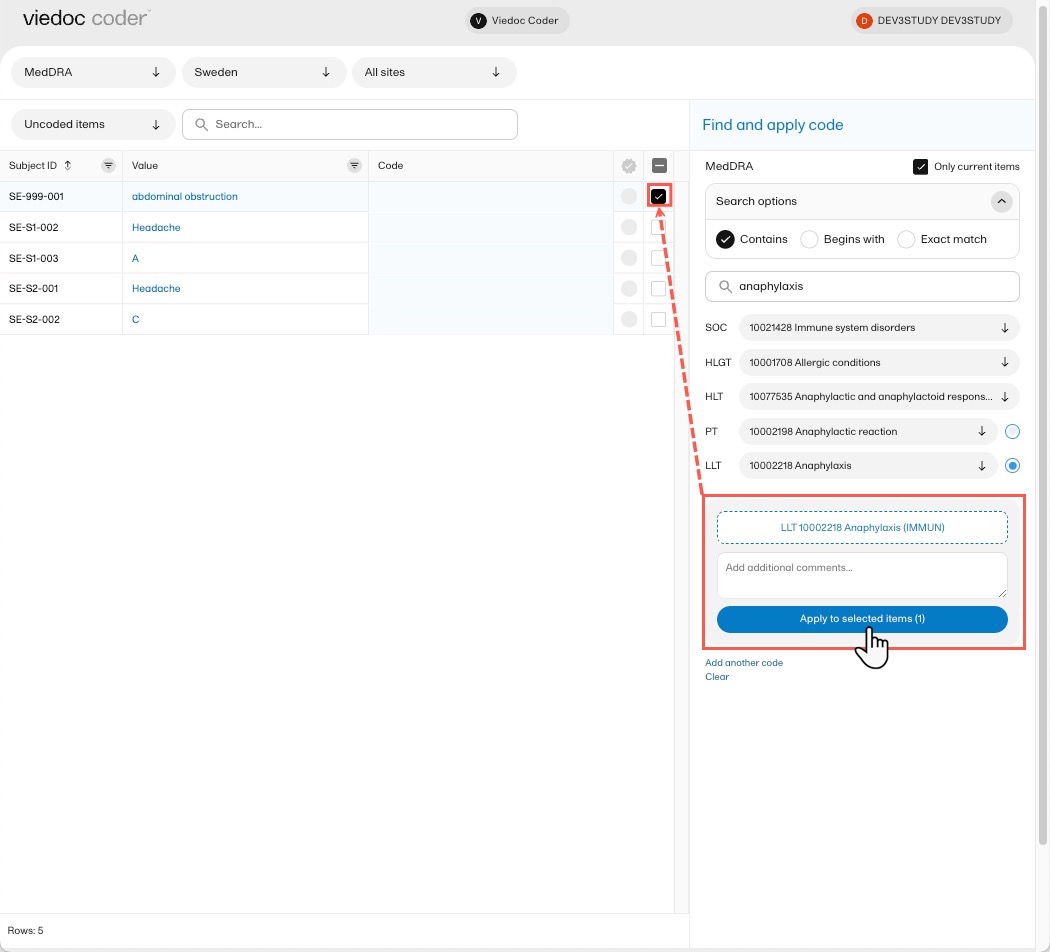
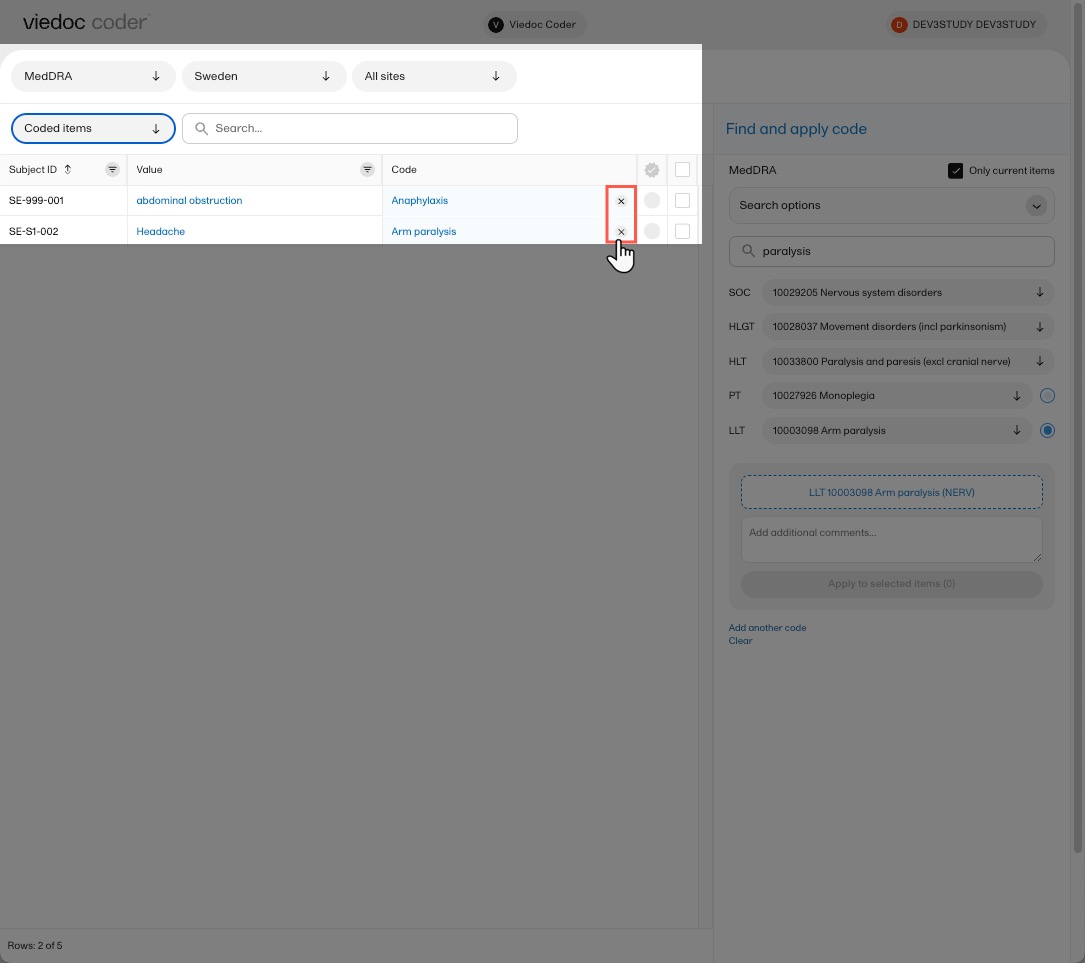
Note! You can remove an applied code by selecting the cross icon to the right of the applied code.
A use case for coding with the WHO Drug Dictionary
| Important! Some WHODrug terminology changes are planned for 2026, therefore some labels and fields have been updated in Viedoc Coder. These updates are available in the new Viedoc Coder only. Users who are still using the old coding console are advised to contact Viedoc to switch to the new Viedoc Coder. |
Searching for a code
To find a code that you want to apply to a value, use the Find and apply code section.
When using WHODrug, you can select to search by:
- Drugs - to search for drugs by their name. This is the default option.
- Active ingredients - to search for drugs by their active ingredients. You can enter multiple ingredients in the search field, separated by
;and the search will return all drugs that contain all specified ingredients.
There are three search options available:
- Contains - the search will return all entries that contain the text typed in the search field. This is the default option.
- Begins with - the search will return all entries that begin with the text typed in the search field.
- Exact match - the search will return all entries that exactly match the text typed in the search field.
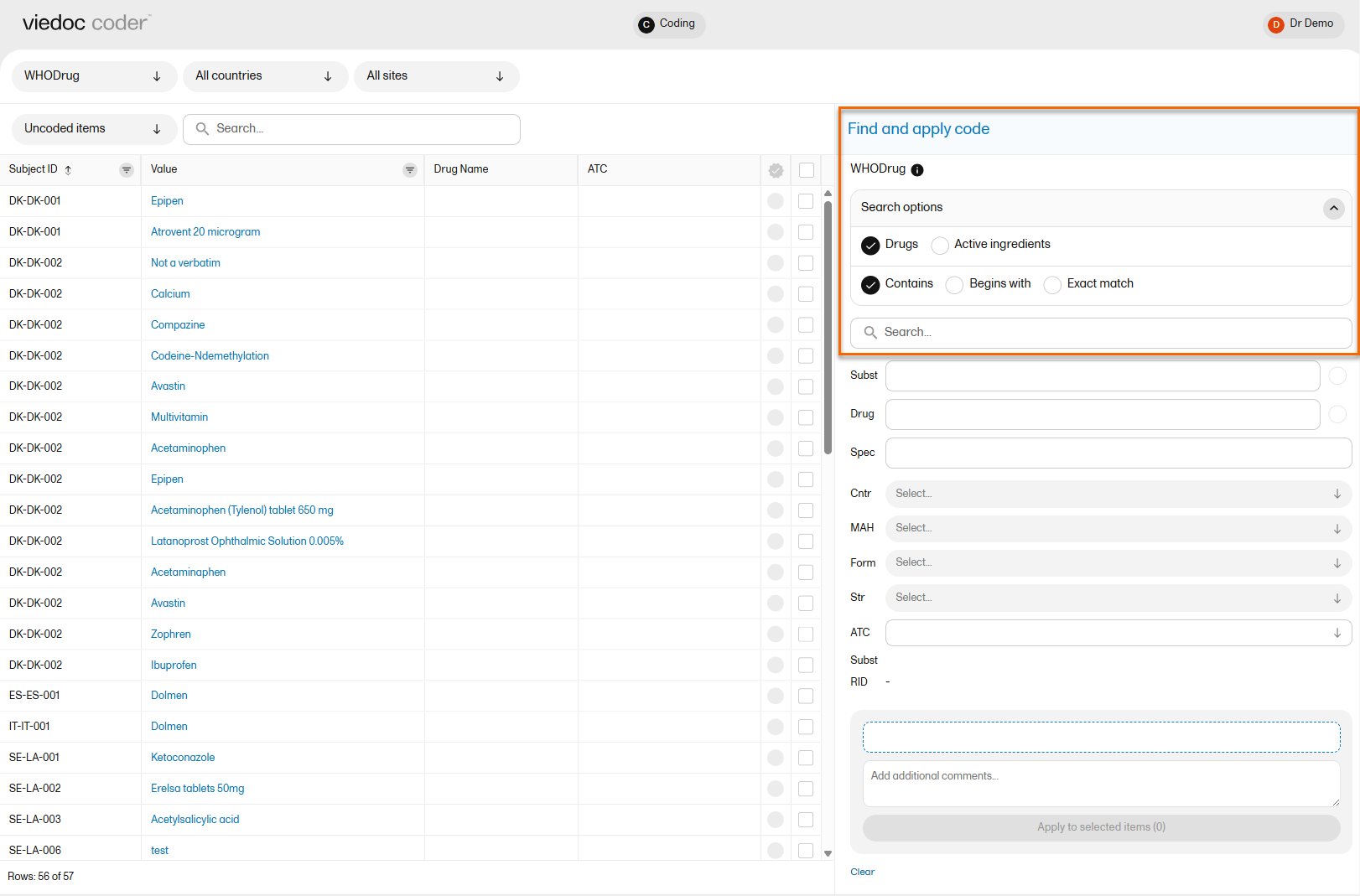
You can search for codes or (substrings of) terms in the Search field. Codes matching the term will be listed in a dropdrown list that deploys from the Search field.
Searching is not case sensitive. If you type in "paRacetaMol", the search can return results such as "paracetamol" or "Paracetamol".
The number behind the entries in the list depicts the number of active ingredients. If you hover the cursor over the number, a dialog box appears that lists the active ingredients:
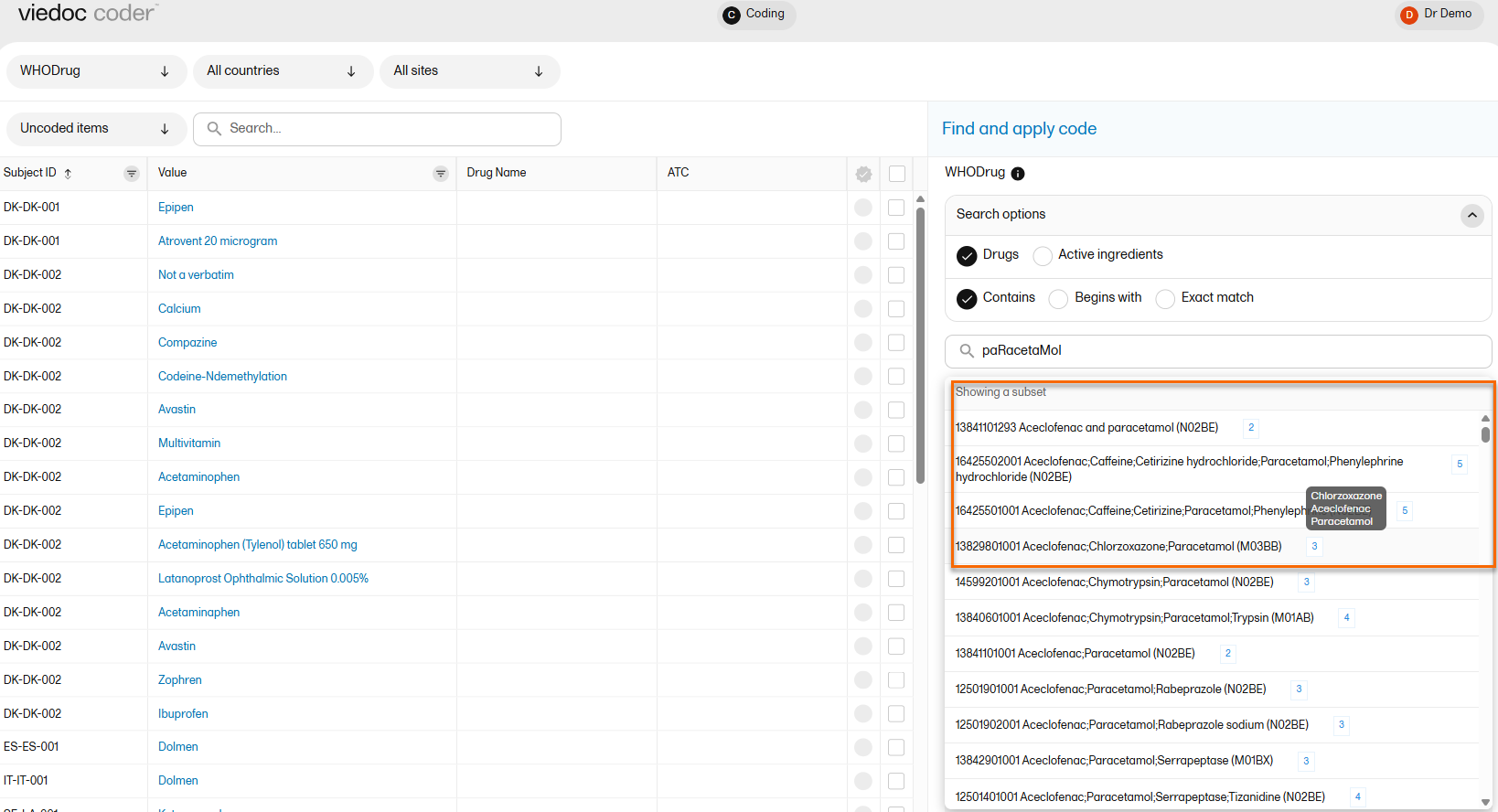
Selecting a code
Select the code (drug) you would like to apply. The details of this drug will appear in the fields below the search field.
In WHODrug, all drugs have a preferred drug. You can select to use the Preferred drug (Pref) or the Drug name by selecting one of the blue radio buttons next to the Pref and Drug fields. Drug is the default.

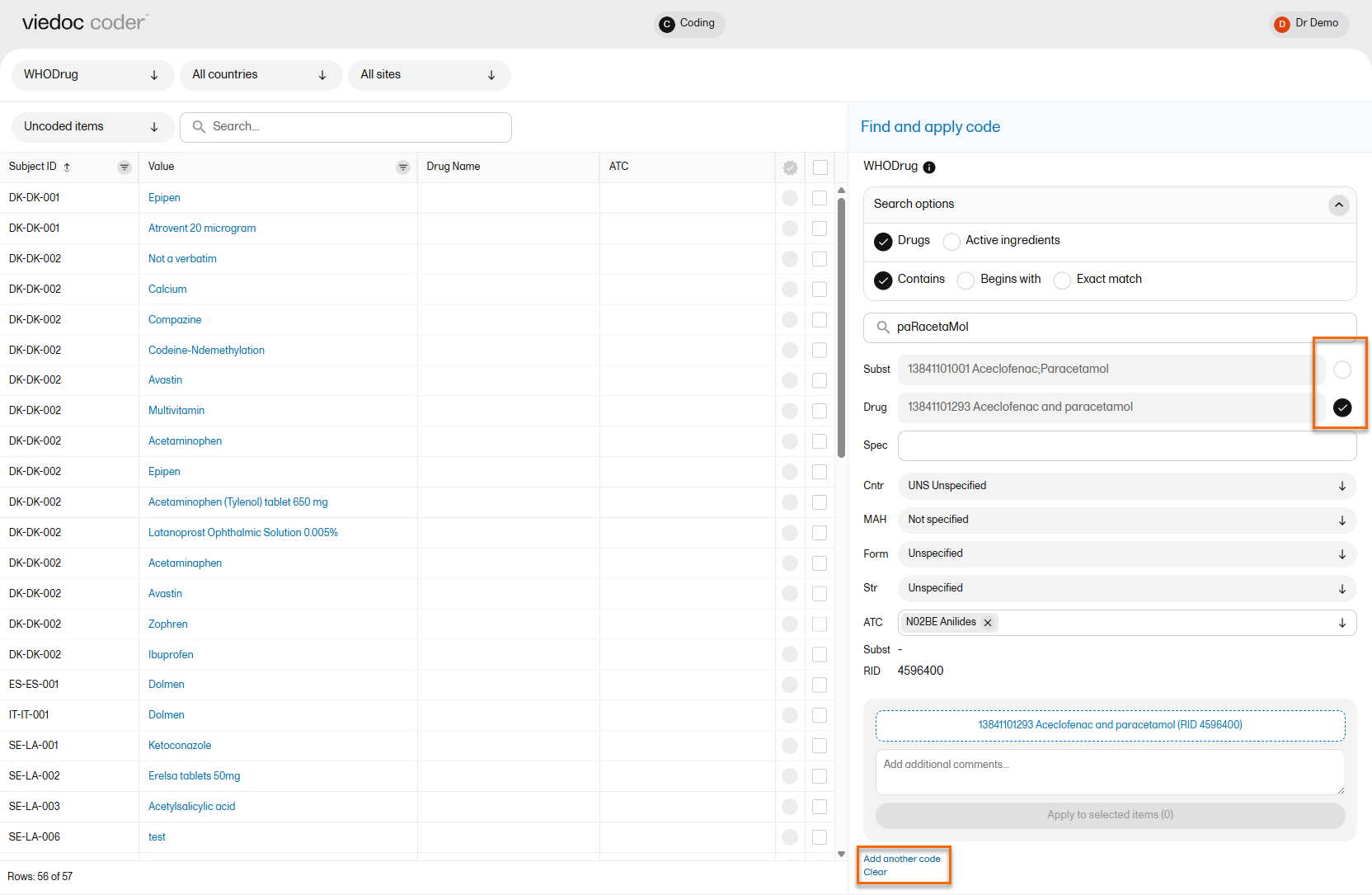
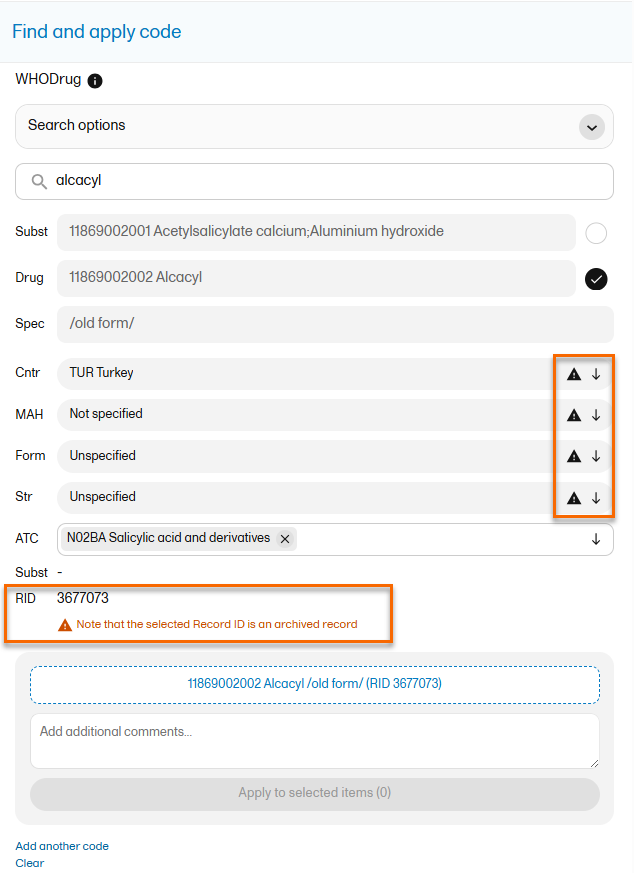
Use the dropdown lists to select Country (Cntr), Marketing Authorization Holder (MAH), Pharmaceutical Form (Form), Strength (Str), or Record ID (RID) , if applicable.
If you would like to add more than one code to the same field, select Add another code.
If you would like to add an interpretation, that is, a comment or explanation of the selected code, select Add interpretation and type your interpretation in the field.
You can reset you selections by selecting Clear.
Tip! If you want to apply a code that has been used before, select that code in the left side of the table. The Find and apply code section is then automatically populated with the selections for that code.
If you selected a drug that carries multiple Anatomic Therapeutic Chemical Classification System (ATC) codes, all ATC codes will be displayed in the ATC field. You can define whether to include all ATC codes in the coding or only a selection. Select the ATC code to include it or select the X icon to remove an ATC code.
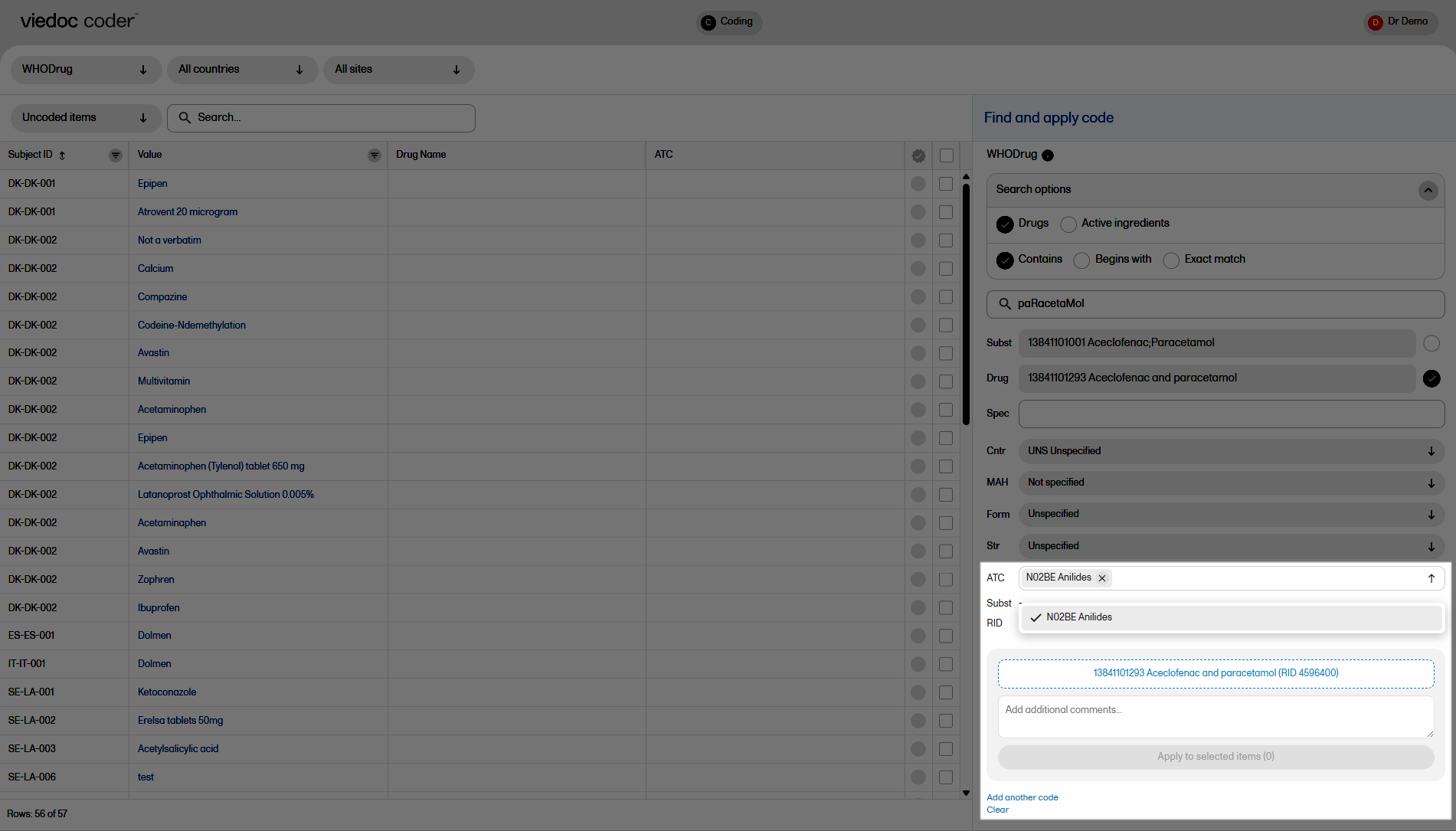
Applying a code
To apply a selected code, select the checkboxes for the value or values you want to apply that code to, and select Apply to selected. The selected code will be applied to the selected subjects and values. The subjects and values can then be found in the Coded items list.
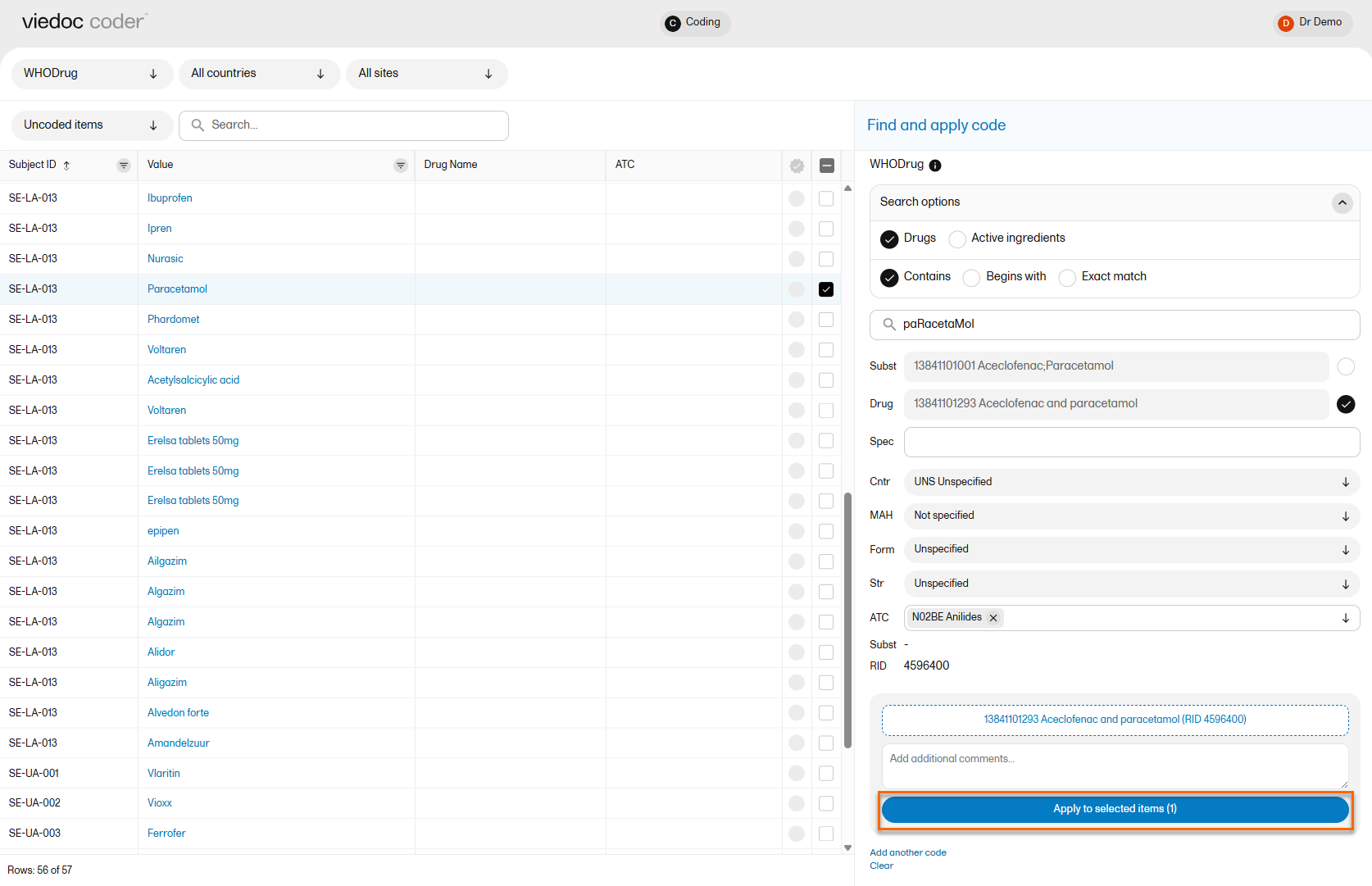
You can remove an applied code by selecting the cross icon to the right of the applied code.
Archived records
Note! For WHODrug dictionary versions from 2026 and later, Old form is no longer shown in the name specifier. Archived records are indicated with a warning triangle regardless of WHO drug version.
Approving the medical coding
After applying codes to the items, you can approve/reject/reset the items as shown in the below table.
| Action | Current state/found in list | New state/found in list |
| Approve |
Coded Rejected |
Approved items |
| Reject |
Coded Approved |
Uncoded items |
| Reset |
Approved Rejected |
Coded items |
Tip! To see all items in one list, select the filter All items.
To approve items that have been coded:
| 1 |
Select the item(s) that you want to approve and select Approve selected: 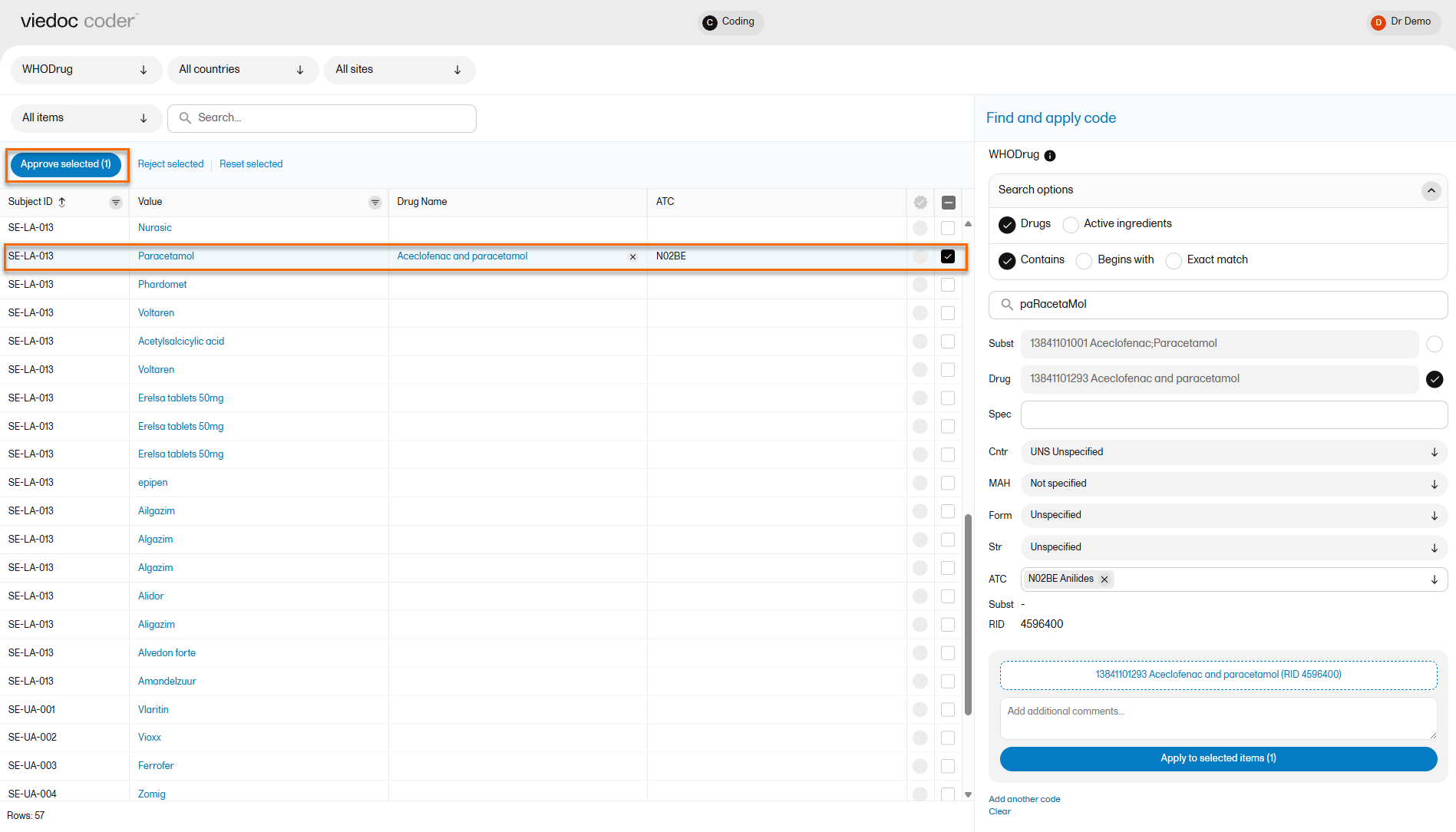
|
| 2 |
The selected item(s) now disappear from the list and are found with the blue "Approved" symbol in the Approved items list. 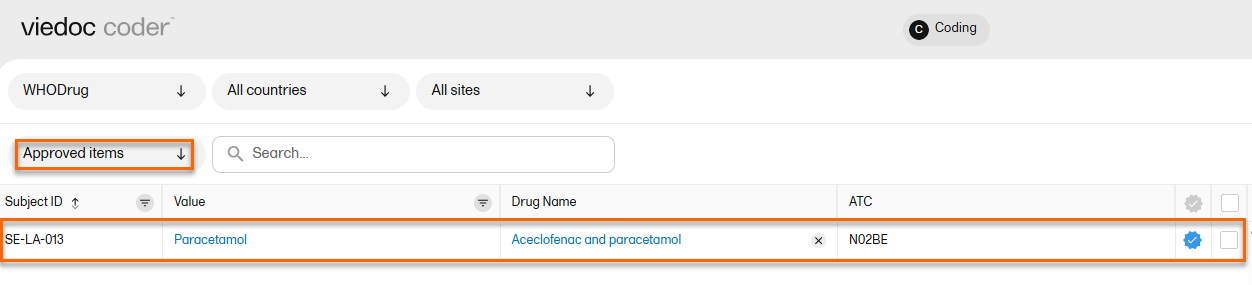
|
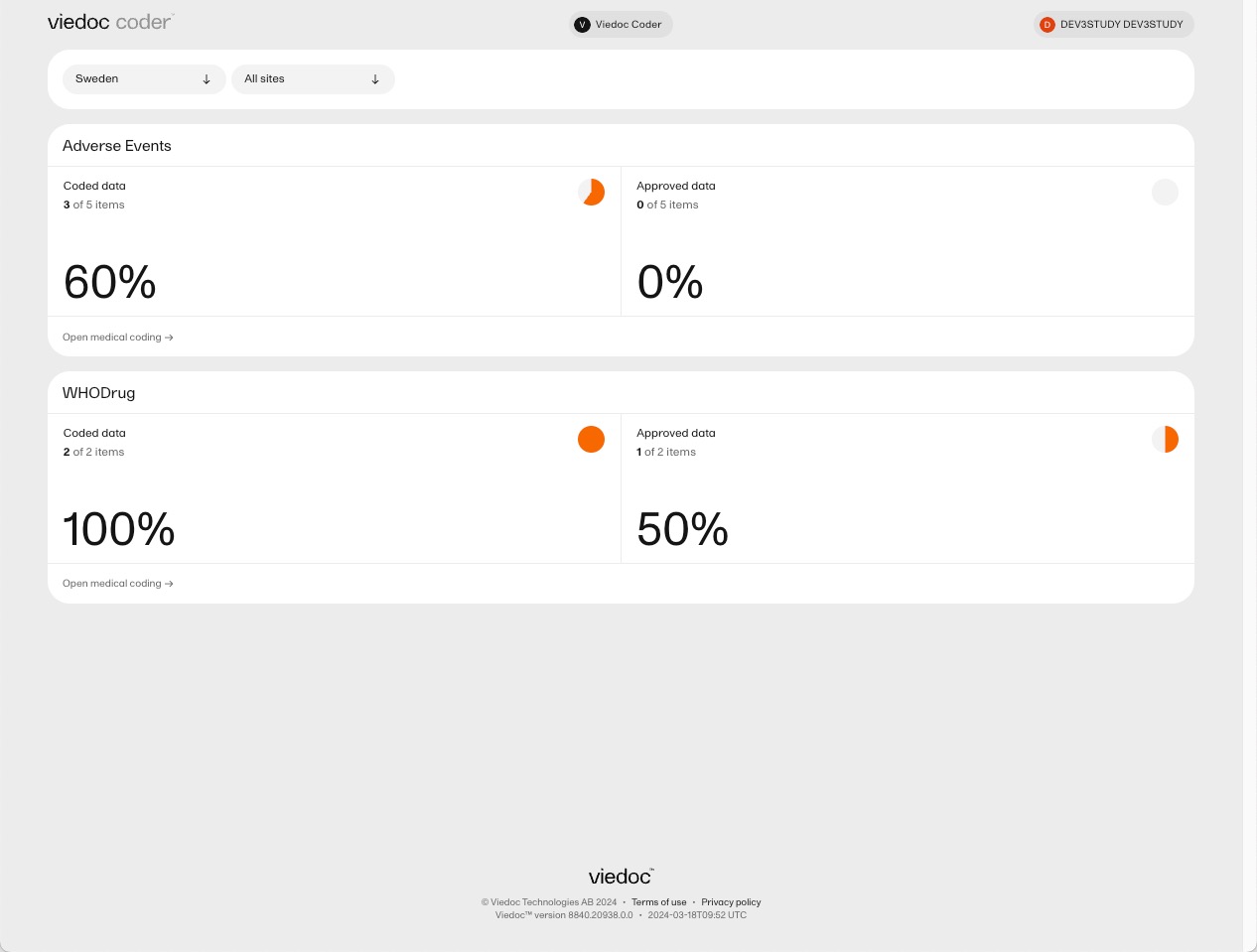
Tip! The metrics of the medical coding that have been approved can be seen on the landing page:
Rejecting the medical coding
To reject items that have been coded:
| 1 |
Select the items that you want to reject and select Reject selected. 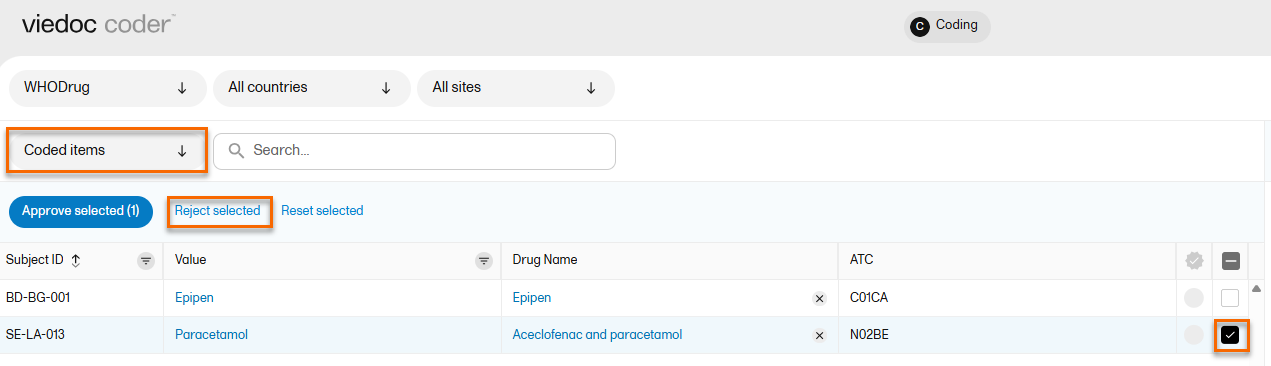
|
| 2 |
The selected item(s) now disappear from the list and are found with the red "rejected" symbol in the Uncoded items list for re-evaluation. 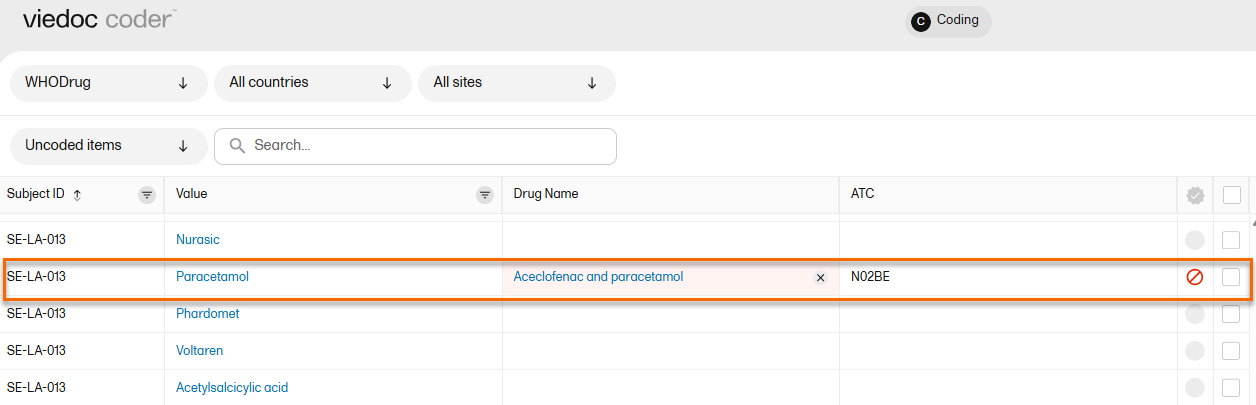
|
Resetting the medical coding
To reset items that have been approved or rejected:
| 1 |
Select the item(s) that you want to reset and select Reset selected. 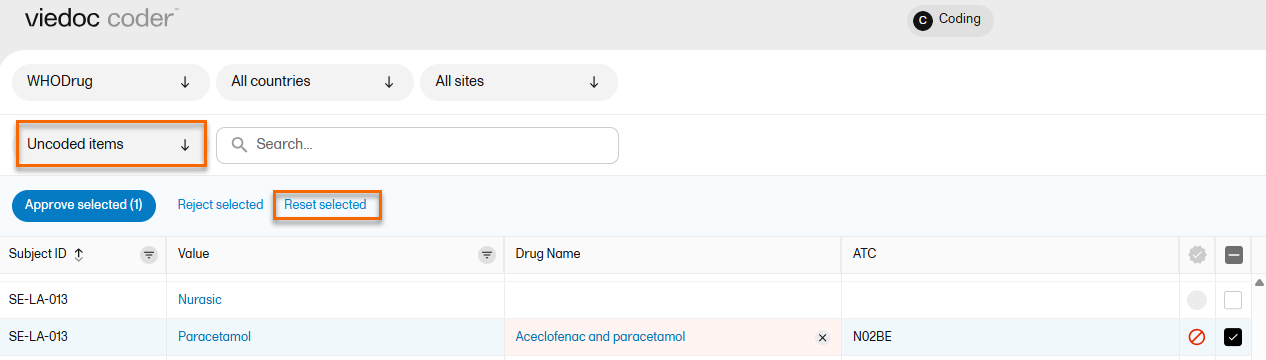
|
| 2 |
The selected item(s) now disappear from the list and are found in the Coded items list without the approved/rejected flag. 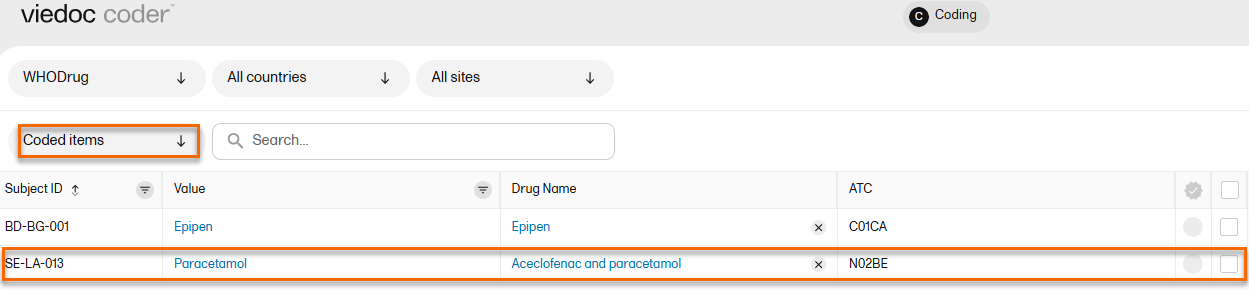
|
Exporting the medical coding
You can export medical coding using Viedoc's data export feature, for more information, see Exporting data.
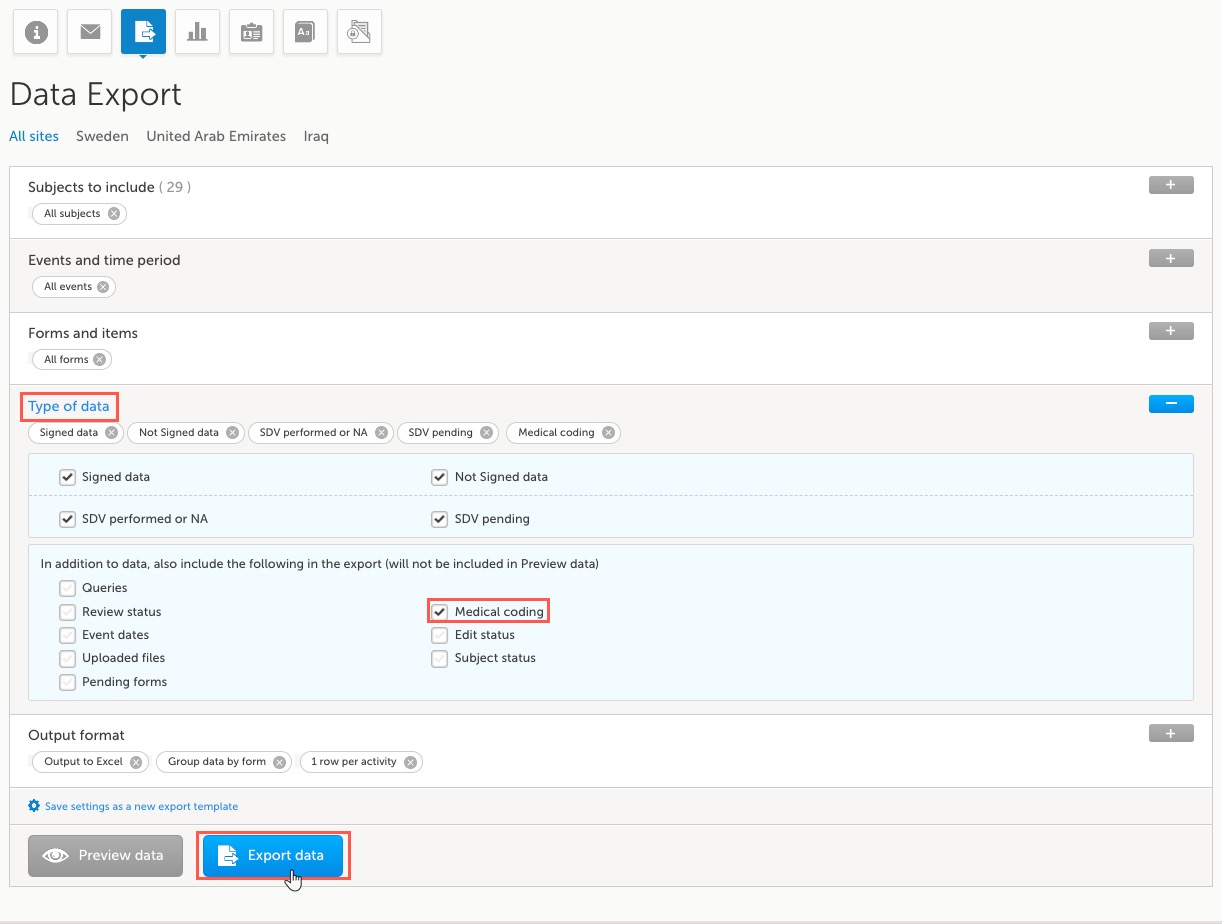
To export the medical coding, select the checkbox in front of Medical coding in the Type of data section.
For more information about how medical coding is exported, see:
Note! You can only export medical coding if permission to export data is activated for your role. If you do not see the data export icon, you do not have a role with export permissions.
Auto coding
In Viedoc Coder, you can choose to enable auto coding. Viedoc supports auto coding for the MedDRA, ATC and WHO Drug dictionaries.
Note! Support for MedDRA-J is planned for inclusion in a future release.
Auto coding can be enabled and disabled for individual scopes within the MedDRA/ATC terminology. Currently, auto coding includes an exact match to MedDRA, any language and ATC, and is applied automatically.
We also support WHODrug Koda, an automated coding service custom-built by UMC. The integration in Viedoc Coder displays WHODrug Koda suggestions to enhance the medical coding.
WHODrug Koda can code both the drug name and the ATC assignment for a specific drug. For more information, see WHODrug Koda
Notes!
- Viedoc supports the WHODrug C3 format. The results received from WHODrug Koda are in the WHODrug B3 format, and Viedoc converts the results to WHODrug C3 before they are displayed in Viedoc Coder.
- WHODrug Koda supports only Latin characters. As a result, studies using WHODrug in Chinese will not return matches for drug names written in non-Latin characters. Please refer to the FAQs about WHODrug Koda about other languages.
For the MedDRA, and ATC dictionaries, auto coding is disabled by default for ongoing studies and enabled for new studies. However, it can be disabled for new studies.
For WHODrug, auto coding is disabled by default.
The auto coding setting is always available in Viedoc Admin, but is only functional for the new Viedoc Coder and not for the old Viedoc Coding console. Please contact your Viedoc representative if you wish to switch to the new Viedoc Coder.
When auto-coding is enabled for your study, all existing uncoded items are auto coded, and all new items are coded automatically without any manual action required.
Note! Items that are auto coded without a match will be flagged, and will still need to be manually coded.
Applying WHODrug auto coded suggestions
To apply an auto coded suggestion:
| 1. | Select the blue radio button. The Apply autocoded suggestions button appears |
| 2. | Select Apply auto coded suggestions to add the item to the coded items: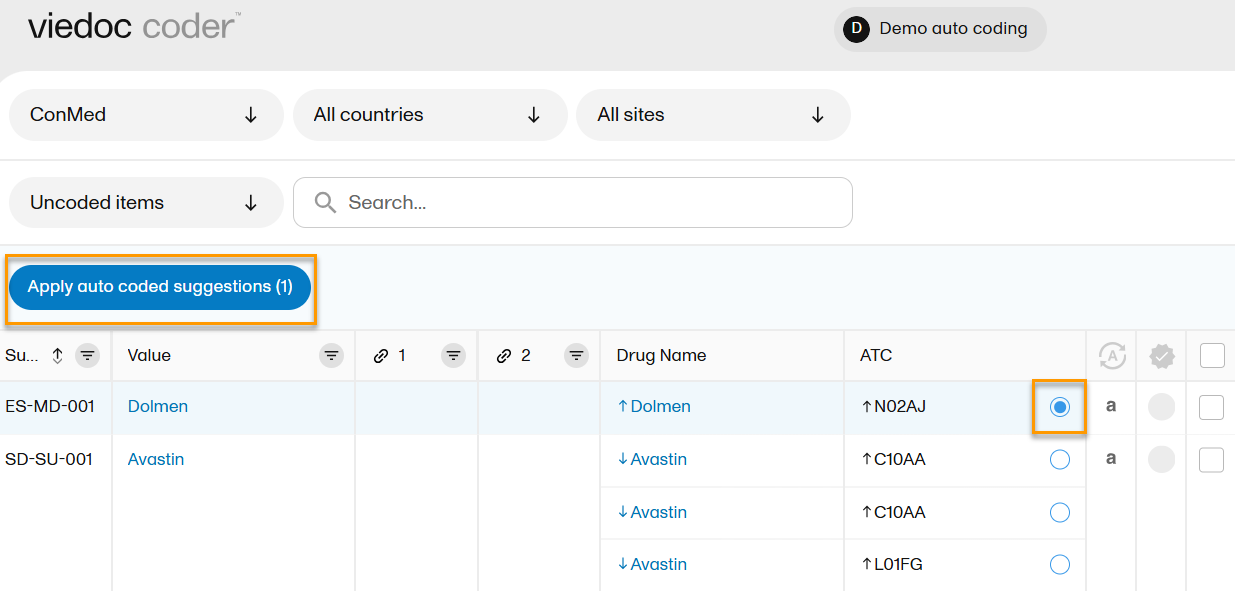 |
The up and down arrows indicate the level of certainty for auto coded items.
An upward arrow signifies a high level of certainty, whereas a downward arrow signifies a lower level of certainty.
Items with a low level of certainty should be reviewed carefully.
An auto coded item is indicated within the column for coded items with the following symbols:
| Symbol | Meaning |
| A | auto coded with a match |
| ! | auto coded without a match and must be manually coded |
| a | suggestion available |
| (empty) | indicates that no auto coding has been run |
WHODrug coding paths
For the available suggestions, hover over the a icon to see a tooltip which describes how WHODrug Koda has found the match:
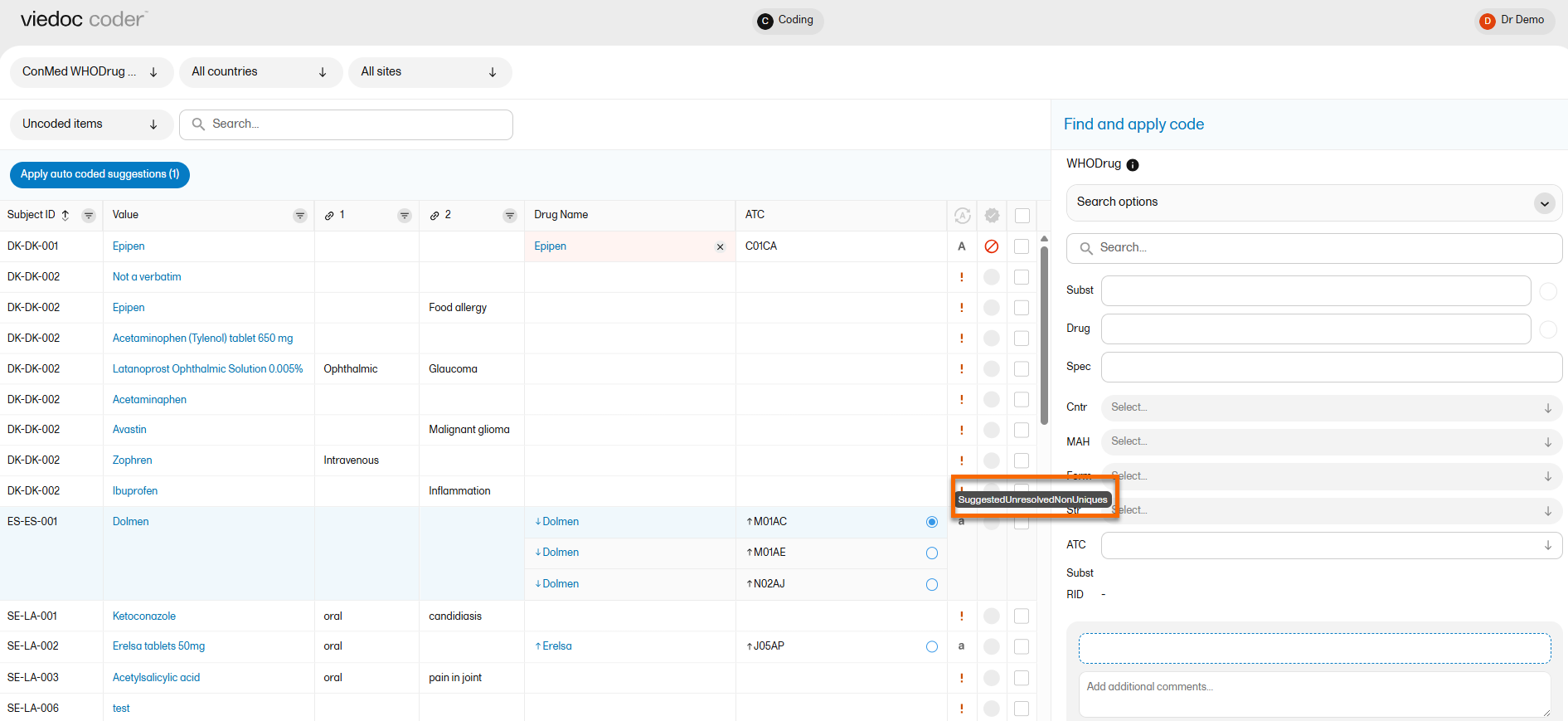
The list of suggested coding paths are as follows:
- Identify drug name
- Direct hit
- Identify ingredients
- Identify form and strength
- Spelling suggestion
- Non-unique solved by indication
- Non-unique solved by route
- Non-unique solved by unsalted drug name
- Non-unique solved by generic rule
- Non-unique solved by preferred base
- Non-unique solved by country
- Uncoded
- Manually coded
- Unresolved non-uniques
- Unfortunate drug name
For more information, see WHODrug Koda
